China's plan to ban solar panel technology export may affect Indonesia's green energy goal
China has been considering to ban the export of several important technologies needed to make solar panels in order to maintain its global dominance and global market share in the sector. The Ministry of Commerce and the Ministry of Science and Technology have imposed the ban on Chinese manufacturers to use their large silicon, black silicon and cast-mono silicon technologies overseas.
Asiatimes.com reported that on December 30, 2022, the technologies were added to a list of items in the "restricted" category in a joint circular on export control published by the science ministry. The commerce ministry proposed in January 2023 to include these technologies in its import and export guidelines to ban more companies from transferring their core silicon technologies overseas.
China is the world's leading manufacturer of solar panel, supplying 80% solar panels and modules for global market. A report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) published in July stated that China accounted for 97% of the world’s wafer production.
Some Chinese solar panel makers moved to Taiwan to try to evade the tariffs but the US expanded its tariffs to apply to the country. They then moved to Cambodia, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam. In June 2022, the US government said it would waive tariffs on solar panels imported to the US from these four countries for 24 months.
Indonesia slowly develops green energy
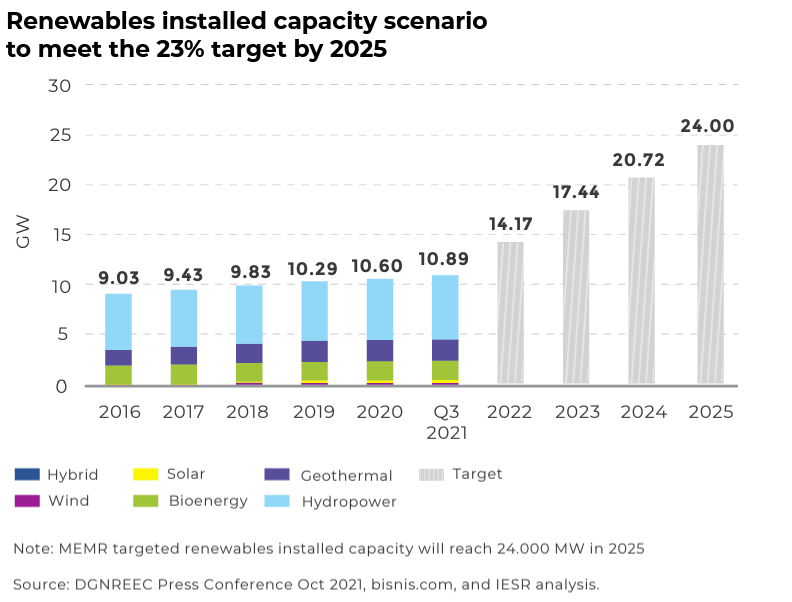
In 2021, Indonesia ranked 17th in the world's most polluted countries. The government has begun to seek renewable energy, including using solar power. In Q3 2021, Indonesia achieved renewable energy capacity of 10.89 GigaWatts (GW), and by 2025 Indonesia is expected to achieve 23% (24GW).
Read also: PLN and Amazon to develop four solar projects in Java and Bali
According to a study by the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources, renewable energy serves as a significant source for the country's national energy security. The potential of renewable energy amounts to 417.8 GW, which comes from:
- Ocean at 17.9 GW
- Geothermal at 23.9 GW
- Bioenergy at 32.6 GW
- Wind power at 60.6 GW
- Hydro power at 75 GW
- Solar power at 207.8 GW
Read also: Pertamina builds 2.25MW solar power at South Sumatra refinery
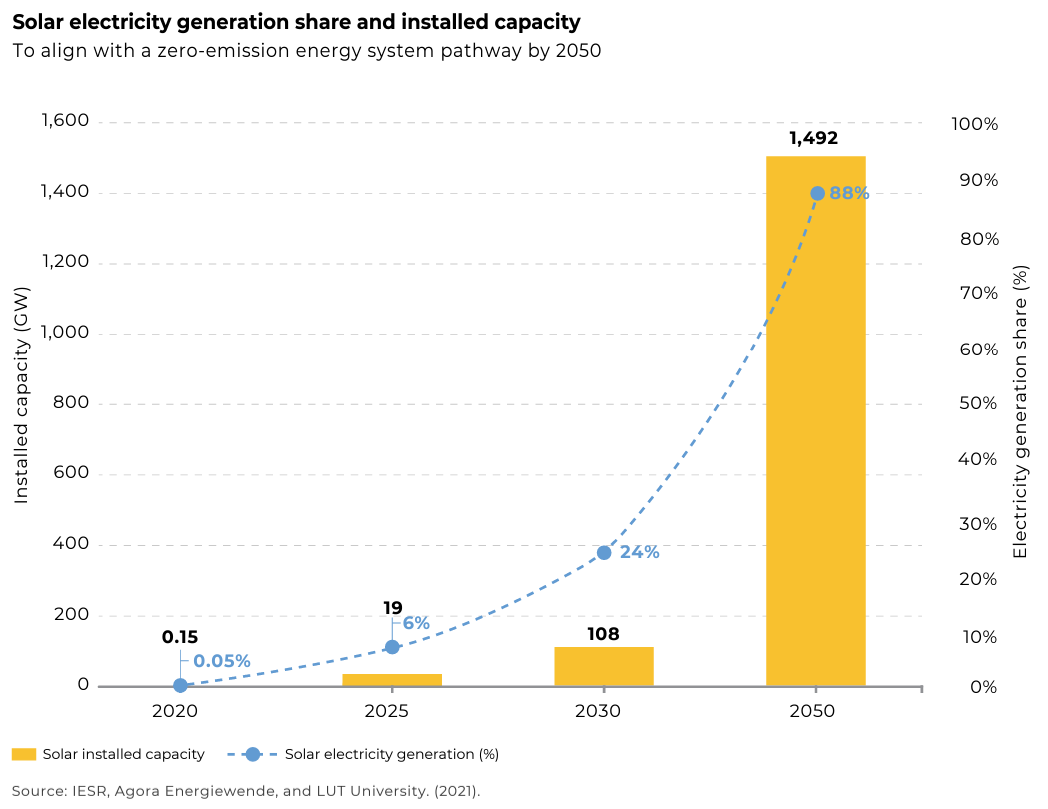
Even though the renewable energy reaches 10.89 GW and the potential for solar power reaches 207.8 GW, only 0.15GW for the installment capacity of solar energy can be produce in 2020. This was due to the relatively small use of solar PV (photovoltaic) caused by the currently high cost of this technology in Indonesia. However, solar PV globally has become increasingly competitive and its deployment can be quite rapid thanks to short construction times. Indonesia plans to install solar PV to reach the capacity to 19 GWp (gigawatt peak) by 2025, 108 GWp by 2030 and 1,492 GWp by 2050.
Core solar panel technologies procurement
With such plan to install solar PV to reach 19 GWp by 2025, Indonesia needs resources and core solar panel technologies, which mainly used to manufacture large solar wafers, black silicon and ultra-high mono-crystalline and multi-crystalline silicon.
In 2021, China was the top importer on the core solar panel technologies, followed by Japan and Malaysia.
| Period | Trade Flow | Reporter | Partner | Trade Value (US$) | Net Weight(Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | M | Indonesia | China | 126,819,115 | 16,729,747 |
| 2021 | M | Indonesia | Japan | 33,425,327 | 112,256 |
| 2021 | M | Indonesia | Malaysia | 17,008,170 | 161,643 |
While data on the China-Indonesia trade is as followed:
| Period | Trade Flow | Reporter | Partner | HS code | Trade Value (US$) | Net Weight(Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | M | Indonesia | China | 854140 | 126,819,115 | 16,729,747 |
| 2020 | M | Indonesia | China | 854140 | 52,145,725 | 7,512,518 |
| 2019 | M | Indonesia | China | 854140 | 49,202,801 | 7,057,843 |
| 2018 | M | Indonesia | China | 854140 | 63,549,737 | 9,006,189 |
While China's export ban has yet taken into effect, Indonesia can further develop its solar power plant to reaching the 19 GWp goal by 2025. In the meantime, Indonesia should seek alternatives for the technology source to process and manufacture large solar wafers, black silicon and ultra-high mono-crystalline and multi-crystalline silicon. It will be a set back if Indonesia failed to obtain and develop the technology to support the government's plan for using solar power.
Already have an account? Sign In
-
Start reading
Freemium
-
Monthly Subscription
30% OFF$26.03
$37.19/MonthCancel anytime
This offer is open to all new subscribers!
Subscribe now -
Yearly Subscription
33% OFF$228.13
$340.5/YearCancel anytime
This offer is open to all new subscribers!
Subscribe now






